What You Need To Know about Brain Inflammation
- Home
- Blog

When you think of the word “inflammation,” what do you picture first? Inflamed joints of an arthritic patient? Someone suffering from an allergic reaction? Or perhaps redness and swelling from an insect bite? Whatever comes to mind, the picture probably isn’t positive.
But not all inflammation is bad. In fact, acute inflammation is a part of the natural protective process in the body that helps our immune system defeat foreign invaders from making us sick. It turns itself on to destroy them, and then turns itself off.
When inflammation becomes chronic (think of “COVID long haulers”), however, it doesn’t just impact our bodies; it can have major consequences on our brains as well. Brain inflammation may even contribute to and worsen a whole host of mental conditions, from depression and bipolar disorder, to PTSD and OCD, to dementia and even schizophrenia.
In this blog, we’ll take a look at the difference between good and bad inflammation, and what you can do if brain inflammation is impacting your mental health.
The Benefits of Acute Inflammation
Acute inflammation is part of your body’s defense system against irritants, bacteria, and viruses. For instance, if you fall and scratch your knee, contaminating the wound with bacteria, the immune system activates to “clean up” the damaged skin and destroy the germs. Your skin may turn red and swell up. This is a sign things are working as they should.
Once your inflammatory response subdues the germs, your body sends out anti-inflammatory agents that begin the healing process. When your immune system works properly, there is a balance between inflammation and these anti-inflammatory agents. Inflammation occurs, but it has a natural end point.
The Consequences of Chronic Brain Inflammation
Sometimes, however, the body gets stuck in the inflammatory process, and that natural end point never arrives. In this case, individuals often develop chronic inflammation. Over time chronic inflammation can lead to the damage or destruction of tissues. In the body, this can lead to cardiovascular disease, or even cancer. In the brain, it can lead to neurodegenerative diseases and mood and anxiety disorders.
When you are suffering from brain inflammation, it’s as if your brain is on fire, and the flames are destroying the most valuable property you own: your brain cells and your mental health. Brain inflammation can be triggered by chronic stress, alcohol abuse, obesity, a diet high in simple carbs, unregulated blood sugar, and more.
If any of these triggers sound familiar, or if you are suffering from depression, anxiety, or worried about the early onset of Alzheimer's and dementia, you may be wondering what you can do to put out the “fire” in your brain. Luckily, there are several interventions shown to decrease chronic brain inflammation, many of which you can take advantage of right away.
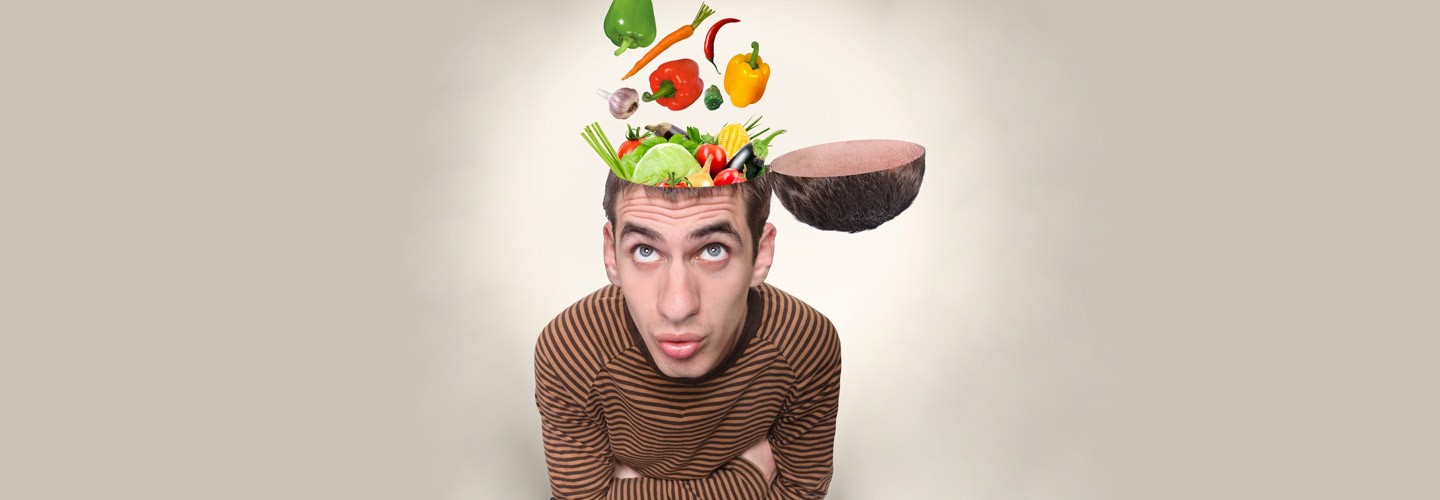
Fight Brain Inflammation with Nutritional and Lifestyle Interventions
A number of foods have been shown to fight brain inflammation, including:
- Oily fish such as salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines
- Dark green veggies such as Swiss chard, kale, and broccoli
- Yogurt with probiotics (helps with gut inflammation, often translating to brain inflammation)
- Beets (helps reduce inflammation and protect against cancer and heart disease)
- Red or yellow onions
- Fruits, especially berries
Lifestyle factors, such as reducing stress through meditation or regular exercise, have also been shown to reduce inflammation. Meditation helps to stop the “danger” signals our brain puts out when we are stressed, and exercise helps get rid of the inflammatory hormones that are released under stress.
While acute inflammation can protect you from infection, chronic inflammation can lead to destructive health outcomes. Adopting a healthy anti-inflammatory lifestyle helps turn off the brain inflammation response and leads to better mental health.
.png?width=144&height=144&name=Untitled%20design%20(34).png)